energy metabolism during endurance sports
As the energy comes from food into the body and the bike on the road?
 The human body is in many ways a miracle thing. It's amazing how it is possible to benefit from a few oats and water, the energy to drive a bike up a mountain. Or that if one "fills in broth" with a baby everything arises from it - hair, muscles, bones, teeth, etc.
The human body is in many ways a miracle thing. It's amazing how it is possible to benefit from a few oats and water, the energy to drive a bike up a mountain. Or that if one "fills in broth" with a baby everything arises from it - hair, muscles, bones, teeth, etc. The following information is culled from books and websites. I am neither a doctor nor a biologist - The following article is hence "with no guarantee of accuracy '... Thematically, the topic "from back to front" described - from the muscle contraction to the photosynthesis.
parts of the illustrations are courtesy of the publisher " trade and technology" from the book 'basic issues of food' (Cornelia A. Schlieper) removed.
1) mechanism of muscle contraction
 The movement of muscles by the displacement of protein molecules actin ( we ) and myosin ( we ) causes. The two thread-like molecules move past each other. The energy for movement of about 8 nm originates from the breakdown of a molecule ATP (adenosine triphosphate ) to ADP (adenosine diphosphate ) .
The movement of muscles by the displacement of protein molecules actin ( we ) and myosin ( we ) causes. The two thread-like molecules move past each other. The energy for movement of about 8 nm originates from the breakdown of a molecule ATP (adenosine triphosphate ) to ADP (adenosine diphosphate ) . The movement of the two molecules takes place in several phases - the so-called cross-bridge cycle. The 'head' of the myosin molecule jumps between contacts on the actin molecules (the illustration to the right comes from the English Wikipedia article ). This cycle can run 10-100 times per second (if enough ATP is available). The process is controlled by electrical charges, the nerve cells come in the form of calcium ions into the muscle cells.
 The ATP molecule is thus something like the "fuel" of the human body and actin / myosin, the pistons in the engine. In contrast to the car, the human body is its fuel through a variety of biochemical processes, but even her - for example from oatmeal.
The ATP molecule is thus something like the "fuel" of the human body and actin / myosin, the pistons in the engine. In contrast to the car, the human body is its fuel through a variety of biochemical processes, but even her - for example from oatmeal. muscle fibers consist of a variety of such actin / myosin molecules (plus 'passive' proteins such as eg. The giant titin molecule ), which are arranged in various forms. The smallest unit is called sarcomere.
 train endurance athletes especially those of ST fibers ('slow twitch' or 'slow twitch') existing parts of the 'striated skeletal muscles '. This muscle fiber type is designed for relatively slow long-term performance.
train endurance athletes especially those of ST fibers ('slow twitch' or 'slow twitch') existing parts of the 'striated skeletal muscles '. This muscle fiber type is designed for relatively slow long-term performance. Links:
- contractile mechanism ( we ) (the drawing is from the right side)
- introduction and animations of myosin / actin (L2 )
- " conversion of biochemical energy into mechanical work, publication of the Institute MaxPlank.
- schematic drawing of a muscle L2
 And of course not only humans this mechanism - the movements of most living things rely on it. This is probably the reason why the genetic of, for example. a hamster and a human are similar in so many areas. The 'platform of life' is based on complex basic mechanisms that function virtually the same in all living creatures. The various forms of life are different then the scaling of various parameters from each other.
And of course not only humans this mechanism - the movements of most living things rely on it. This is probably the reason why the genetic of, for example. a hamster and a human are similar in so many areas. The 'platform of life' is based on complex basic mechanisms that function virtually the same in all living creatures. The various forms of life are different then the scaling of various parameters from each other. 2) energy metabolism
2.1) energy production in the cell -. Overview
 In the cell, degradation products of the food in a multistage Process 'burned'. The mechanism that provides the energy, the conversion of carbon compounds (molecules with large chemical energy) in CO2 and water (molecules of low chemical energy). Original components of energy metabolism are prepared by the digestive food components: short-chain carbohydrates , amino acids and fatty acids (illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper).
In the cell, degradation products of the food in a multistage Process 'burned'. The mechanism that provides the energy, the conversion of carbon compounds (molecules with large chemical energy) in CO2 and water (molecules of low chemical energy). Original components of energy metabolism are prepared by the digestive food components: short-chain carbohydrates , amino acids and fatty acids (illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper). The utilization of nutrients into energy in the cell is a three-step process. In the first stage, the initial products in a few "Basic fuel molecules" converted. The substance acetyl-CoA is one of the most important fuel - it is more or less the "hub" in the processing of carbohydrates, fats, and (some) proteins dar.
 In the second step of the "basic fuels" so-called " citrate cycle" carbon and hydrogen atoms are split off. The "citric acid cycle is a chain of nine chemical reactions. The carbon atoms combine with oxygen to form CO2. Remarkably, that is required for the breakdown of fat is a breakdown product of carbohydrates ( oxaloacetate ). The statement that "fat burns in the fire of carbohydrates" is from this effect (Illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper).
In the second step of the "basic fuels" so-called " citrate cycle" carbon and hydrogen atoms are split off. The "citric acid cycle is a chain of nine chemical reactions. The carbon atoms combine with oxygen to form CO2. Remarkably, that is required for the breakdown of fat is a breakdown product of carbohydrates ( oxaloacetate ). The statement that "fat burns in the fire of carbohydrates" is from this effect (Illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper).  In the third stage - the so-called respiratory chain - be in the citric acid cycle split-off hydrogen atoms in the mitochondria (cell components) with oxygen connected to water - similar to a fuel cell (illustration from ' basic issues of food 'by Cornelia A. Schlieper).
In the third stage - the so-called respiratory chain - be in the citric acid cycle split-off hydrogen atoms in the mitochondria (cell components) with oxygen connected to water - similar to a fuel cell (illustration from ' basic issues of food 'by Cornelia A. Schlieper). 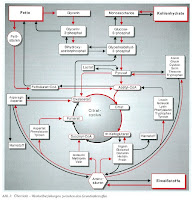 is amazing to me that a few basic mechanisms are sufficient for the life of this beautiful earth with energy. All nutrients are first in the basic components split and then fed into a cycle of chemical reactions. It fills up a pulp and get everything in the world happened out below - is not - a great thing? The graph on the right I particularly like - half a page, you can outline the mechanism provides us with energy (Illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper).
is amazing to me that a few basic mechanisms are sufficient for the life of this beautiful earth with energy. All nutrients are first in the basic components split and then fed into a cycle of chemical reactions. It fills up a pulp and get everything in the world happened out below - is not - a great thing? The graph on the right I particularly like - half a page, you can outline the mechanism provides us with energy (Illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper). other publications.
- " The Muscular energy supply in the sport ," Dr. Moos
- " The energy metabolism ," Dr. Moos
2.2) carbohydrate metabolism
 After Pre-processing through the digestive system make it the short-chain carbohydrates glucose, galactose and fructose into the cell. Lt. C. Schlieper takes the body a day about 200-250g of glucose, galactose and 10-15g 30-60g fructose. The body can store a part of the absorbed carbohydrates in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscle cells - and glucose even create its own (' gluconeogenesis ') - for example, degradation products of fats or proteins - or glucose in fat or convert amino acids. The degradation of glucose for energy in pyruvate is called glycolysis (Illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper).
After Pre-processing through the digestive system make it the short-chain carbohydrates glucose, galactose and fructose into the cell. Lt. C. Schlieper takes the body a day about 200-250g of glucose, galactose and 10-15g 30-60g fructose. The body can store a part of the absorbed carbohydrates in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscle cells - and glucose even create its own (' gluconeogenesis ') - for example, degradation products of fats or proteins - or glucose in fat or convert amino acids. The degradation of glucose for energy in pyruvate is called glycolysis (Illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper). 2.3.) fat metabolism
 in the form of fat the body stores energy in the long term. If you take absolutely no nourishment can survive approximately 200g fat per day. Also fatty acids can make the body itself to store excess carbs for lean times (for example, in the form of triglycerides ) - this process is called lipogenesis . The reduction of fat is called lipolysis . Fatty acids are more human by the amount of energy the most important energy supplier Cells. For the degradation of fatty acids must first be expended energy in the form of ATP before release energy in the form of ATP. Fats and carbohydrates in energy metabolism hang closely together - the molecules are important nodes acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate (illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper).
in the form of fat the body stores energy in the long term. If you take absolutely no nourishment can survive approximately 200g fat per day. Also fatty acids can make the body itself to store excess carbs for lean times (for example, in the form of triglycerides ) - this process is called lipogenesis . The reduction of fat is called lipolysis . Fatty acids are more human by the amount of energy the most important energy supplier Cells. For the degradation of fatty acids must first be expended energy in the form of ATP before release energy in the form of ATP. Fats and carbohydrates in energy metabolism hang closely together - the molecules are important nodes acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate (illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper). goes in several publications of the sports physician Dr. Moos one on the topic of fat metabolism during exercise. He criticized the possibility the myth of the 'heart rate zone is burned in the fat' or that 'fat burning begins only after 20 minutes'. The fat metabolism is always active, not only in the so-called 'fat burning zone', or only after some time. If you want to remove you just have to eat fewer calories than you consume ...:
- " fat burning in the sport, myth and truth "
- " Heart Rate: Is it the fat burning zone while exercising ?
2.4.) Protein metabolism
 proteins are broken down by digestion into its component amino acids and transported via the bloodstream into the cells. In addition, a conversion takes place in the body permanently instead of proteins. Lt. C. Schlieper takes the body approximately 125g per day amino acids, reduced by some 500 g amino acids, which are already in the body "burns" about 125g. This part of the molecular constituents ' amino ' is cleaved and bound in urea. The remaining balance molecule is then fed into the citric acid cycle (illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper).
proteins are broken down by digestion into its component amino acids and transported via the bloodstream into the cells. In addition, a conversion takes place in the body permanently instead of proteins. Lt. C. Schlieper takes the body approximately 125g per day amino acids, reduced by some 500 g amino acids, which are already in the body "burns" about 125g. This part of the molecular constituents ' amino ' is cleaved and bound in urea. The remaining balance molecule is then fed into the citric acid cycle (illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper). proteins are built on demand from free amino acids. Non-essential amino acids can be produced by the body. Essential amino acids however have to be supplied through food. From the free amino acids, the body new proteins by producing a copy of the pattern of RNA -section - a part of a DNA molecule - one part of the human genome encoded program of life. The free Amminosäuren store on to a mRNA molecule - which has previously been replaced as a zip of a DNA molecule. .
- " protein metabolism ," Dr. Moos
2.5) Multi-stage energy storage body
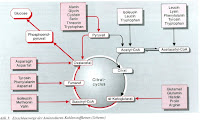
Some very interesting articles on energy supply can be found on the homepage of Dr. Moos - particularly appropriate is the publication ' Muscular energy supply during exercise '. Important for the following paragraphs is: the mechanisms to run always from each other, the anaerobic splitting of glucose does not hear abruptly when the aerobic cleavage begins. But with different exercise duration and intensity outweigh individual mechanisms.
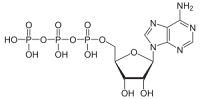 Stage 1: ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Stage 1: ATP (adenosine triphosphate) As described above, transfer chemical energy from food constituents on ATP and in areas such as muscle contraction re-released. ATP itself is only in low concentration in the cell. ATP is and will be transferred from "memory drugs" restored. The energy extraction from the available ATP in muscle is sufficient for 1-2 seconds. Weightlifting use eg. primarily this energy source.
Level 2: CP (creatine phosphate)
 The first source for the production of ATP is CP (creatine phosphate) . By the 'transfer' of the phosphate group to an ADP molecule is again from creatine phosphate creatine, and ATP from ADP - and the basic component of a muscle fiber may subsequently move 8 nm wide. The stocks of KP in the muscle cell are exhausted after about 7 seconds - not even Usain Bolt can run alone with this energy source 100 meters away.
The first source for the production of ATP is CP (creatine phosphate) . By the 'transfer' of the phosphate group to an ADP molecule is again from creatine phosphate creatine, and ATP from ADP - and the basic component of a muscle fiber may subsequently move 8 nm wide. The stocks of KP in the muscle cell are exhausted after about 7 seconds - not even Usain Bolt can run alone with this energy source 100 meters away. Level 3: Anaerobic Degradation of glucose / pyruvate
 Everything beyond the sprint in the saving cavity after the sight of the saber-toothed tiger requires the degradation of storage substances, such as glycogen (or of its degradation product pyruvate ). Pyruvate can (short term) without oxygen in lactate and ATP or (longer term) with oxygen in the acetyl-CoA and ATP are converted.
Everything beyond the sprint in the saving cavity after the sight of the saber-toothed tiger requires the degradation of storage substances, such as glycogen (or of its degradation product pyruvate ). Pyruvate can (short term) without oxygen in lactate and ATP or (longer term) with oxygen in the acetyl-CoA and ATP are converted.  The energy storage level 3 are enough for about 30-40 seconds. This is probably the reason why 400m or 800m races are so hard - you try as much as possible to come with the anaerobic energy, the resulting lactate is then more and more obstacles. Lactate inhibits an important enzyme of carbohydrate metabolism. The more lactate is present, the more difficult it further energy obtained in this way. Middle-distance runners train the body in the most efficient removal of lactate.
The energy storage level 3 are enough for about 30-40 seconds. This is probably the reason why 400m or 800m races are so hard - you try as much as possible to come with the anaerobic energy, the resulting lactate is then more and more obstacles. Lactate inhibits an important enzyme of carbohydrate metabolism. The more lactate is present, the more difficult it further energy obtained in this way. Middle-distance runners train the body in the most efficient removal of lactate. Level 4: Aerobic degradation of glucose / pyruvate
 The aerobic cleavage of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA enough then already quite long - until the glycogen stores of the body are exhausted. A marathon, you can deny it almost. A marathon will be tough when the Glycongen stocks are depleted and the body was not has trained to use the fat stores without question.
The aerobic cleavage of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA enough then already quite long - until the glycogen stores of the body are exhausted. A marathon, you can deny it almost. A marathon will be tough when the Glycongen stocks are depleted and the body was not has trained to use the fat stores without question. Level 5: fat, protein
The fat and protein reserves in the body are usually sufficient to prevent the body about 40 days to supply energy. If you eat nothing for 40 days, a person weighing 75kg is building about 14-15kg fat and protein to sustain life.
2.6.) Hormones
Hormones are chemical messengers that communicate through the various body parts together. Hormones are usually constructed from Amminosäuren. Various glands produce hormones, plays a central role in the pituitary . Hormones are primarily via the blood circulation transported. The contact with receptors in organs then lead to reactions. An important hormone in metabolism is insulin . When insulin is released to try organs with insulin receptors (especially the liver), glucose can be seen in the blood and convert it into glycogen, the storage material. The opposite of insulin - glucagon - causes the other hand, increased degradation of glycogen to glucose and release into the blood.
3) digestion
The digestive system converts food into simpler, usable materials for the body.
3.1.) Enzymes
By enzymes are mainly in the mouth, Stomach and small intestine 'great' nutrient molecules into smaller parts divided. The main work take over enzymes from the pancreas (pancreas) generates, in the small intestine to the food act. Through the intestinal wall, the split-nutrient components enter the blood and lymphatic circulation and be transported to the cells. There they are recycled, stored or converted. Non-recyclable nutrients and waste products (eg CO2) are eliminated.
3.2) digestion of carbohydrates
The enzyme amylase -. A component of saliva - separates the mouth and stomach long-chain carbohydrates on. In the duodenum contribute their production of the pancreatic enzymes amylase and glucosidase - the long carbohydrate molecules are further reduced. In the small intestinal wall, including the conversion is completed. Reach the blood stream glucose, galactose and fructose.
3.3.) Digestion of fats
Also in fats, the task of digestion, the captured molecules to break down into simple components. Fat is digested mainly in the small intestine by pancreatic enzymes (lipases) and bile into monoglycerides, glycerol and fatty acids. About the small intestine wall, the fat components in the blood and lymph circulation are included.
3.4.) Digestion of proteins
take over the breakdown of proteins, the enzymes of the group peptidases (pepsin), which act primarily in the stomach. In the small intestine other enzymes of the pancreas and to cleave the proteins into simple amino acids, which enter through the intestinal wall into the blood.
4 .) Elements of food
4.1.) carbohydrates
 carbohydrates are an important consideration in sports energy source. They are chemical compounds of carbon , hydrogen and oxygen and are obtained by means of plant photosynthesis . There are many different carbohydrates that are utilized differently by the body during exercise (fast). Roughly divided according to molecular size carbohydrates. The simpler and smaller the molecule, the easier it can make use of the body.
carbohydrates are an important consideration in sports energy source. They are chemical compounds of carbon , hydrogen and oxygen and are obtained by means of plant photosynthesis . There are many different carbohydrates that are utilized differently by the body during exercise (fast). Roughly divided according to molecular size carbohydrates. The simpler and smaller the molecule, the easier it can make use of the body. monosaccharides (simple sugars)
 monosaccharides are the 'building blocks' of carbohydrates. In addition to a variety of monosaccharides, which are used in the body as an energy carrier, metabolite and cellular component are mainly via food glucose / dextrose (glucose) (about 200g/Tag) galactose (mucus sugar) (about 10g/Tag) and fructose (fruit sugar) (about 30g/Tag) Date.
monosaccharides are the 'building blocks' of carbohydrates. In addition to a variety of monosaccharides, which are used in the body as an energy carrier, metabolite and cellular component are mainly via food glucose / dextrose (glucose) (about 200g/Tag) galactose (mucus sugar) (about 10g/Tag) and fructose (fruit sugar) (about 30g/Tag) Date.  glucose is the principal energy source in metabolism, it is absorbed in the small intestine into the blood. The " blood sugar levels " means the proportion of dissolved glucose in the blood. Increases the glucose content in the blood after eating, is signaled by the hormone insulin the liver and muscle tissue, glucose to "draw" from the blood and store them as glycogen . All carbohydrate species must first be converted by digestive enzymes into glucose to be absorbed into the blood to. This transformation 'delayed' after eating higher quality carbohydrates (eg. strength ) the uptake of glucose into the blood - then you have more energy. If more carbohydrates are needed as our daily diet, the excess is converted into fat and stored.
glucose is the principal energy source in metabolism, it is absorbed in the small intestine into the blood. The " blood sugar levels " means the proportion of dissolved glucose in the blood. Increases the glucose content in the blood after eating, is signaled by the hormone insulin the liver and muscle tissue, glucose to "draw" from the blood and store them as glycogen . All carbohydrate species must first be converted by digestive enzymes into glucose to be absorbed into the blood to. This transformation 'delayed' after eating higher quality carbohydrates (eg. strength ) the uptake of glucose into the blood - then you have more energy. If more carbohydrates are needed as our daily diet, the excess is converted into fat and stored. disaccharides (double sugars)
 Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide molecules. Known about the dietary of this genus are maltose (malt sugar) , sucrose (beet sugar) and lactose (milk sugar) .
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide molecules. Known about the dietary of this genus are maltose (malt sugar) , sucrose (beet sugar) and lactose (milk sugar) . oligosaccharides (Complex sugars) and polysaccharides (multiple sugars)
 carbohydrates are composed of three or more monosaccharides absorbed slowly by the digestive system ( oligosaccharides, polysaccharides ). Representatives are, for example starch , cellulose and in the body used for energy storage glycogen. Glycogen molecule can consist of up to 10,000 glucose molecules.
carbohydrates are composed of three or more monosaccharides absorbed slowly by the digestive system ( oligosaccharides, polysaccharides ). Representatives are, for example starch , cellulose and in the body used for energy storage glycogen. Glycogen molecule can consist of up to 10,000 glucose molecules. play in the sports nutrition dextrin or maltodextrin a role. This refers to a mixture of shorter degradation products of starch or glycogen, consisting of approximately 4 to 40 glucose molecules. Energy gels often contain maltodextrin. By mixing and shorter long-chain molecules, the energy absorption into the bloodstream over a longer period is extended.
4.2.) fats, fatty acids
 fats are substances such as carbohydrates from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Fats called fatty compounds from and alcohols. The type of connection between fatty acid and alcohol molecule called acetate . Fatty acids in turn consist of a hydrocarbon chain and a carboxyl group . Alcohols are also compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, is characteristic for them hydroxy group . The so-called esterification, the oxygen molecule of the OH group combines with a carbon molecule of the carboxyl group of the fatty acid.
fats are substances such as carbohydrates from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Fats called fatty compounds from and alcohols. The type of connection between fatty acid and alcohol molecule called acetate . Fatty acids in turn consist of a hydrocarbon chain and a carboxyl group . Alcohols are also compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, is characteristic for them hydroxy group . The so-called esterification, the oxygen molecule of the OH group combines with a carbon molecule of the carboxyl group of the fatty acid. fatty acids are 'saturated "means, if each carbon molecule is connected to the carbon chain with two hydrogen molecules.
 Unsaturated fatty acids have carbon molecules with only one Wassertoffmolekül and for an additional double bond adjacent to a carbon molecule. Unsaturated fatty acids are more reactive than saturated fatty acids. As with the proteins that fatty acids are called 'essential', that the body needs, but which he can not produce itself.
Unsaturated fatty acids have carbon molecules with only one Wassertoffmolekül and for an additional double bond adjacent to a carbon molecule. Unsaturated fatty acids are more reactive than saturated fatty acids. As with the proteins that fatty acids are called 'essential', that the body needs, but which he can not produce itself. an important fat group in the human body, the so-called mono-, di-and triglycerides - compounds of glycerine - C3H5 (OH) 3 - 1, 2 or 3 fatty acids. triglycerides are stored nutrients in the body. In this form, lies a body of excess energy for lean times in fat cells.
4.3.) proteins / protein, amino acids
 proteins ("protein") are a class of substances that play in the body not only in the diet play an important role. They are the all-rounder in the body - their functions range from "Building the body (bones, muscles ,...) about" biochemical factory "to" fuel ". Proteins consist of amino acids .
proteins ("protein") are a class of substances that play in the body not only in the diet play an important role. They are the all-rounder in the body - their functions range from "Building the body (bones, muscles ,...) about" biochemical factory "to" fuel ". Proteins consist of amino acids . proteins are made up of chains of amino acids . Amino acids are a class of organic chemical compounds, with two distinctive components ( COOH and NH2 ). Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins are called "proteinogenic", the many other "non-proteinogenic". In humans, there are 21 amino acids, 9 of which the body can not produce themselves - they are referred to as " esenzielle amino acids.
 proteins can consist of several thousand amino acids (the largest known protein titin has about 30,000 amino acids). For 'short' chains of molecules, proteins bezeichet as peptides. The structure of proteins (the sequence of amino acids that make up the molecule) per protein is in a gene set - a section in the DNA - the carrier of genetic information.
proteins can consist of several thousand amino acids (the largest known protein titin has about 30,000 amino acids). For 'short' chains of molecules, proteins bezeichet as peptides. The structure of proteins (the sequence of amino acids that make up the molecule) per protein is in a gene set - a section in the DNA - the carrier of genetic information. On food proteins, for example, when eating meat, fish, eggs, dairy products and nuts are included. During digestion they are broken down into amino acids that are transported by the blood into the cells. In the cells they will then use the genetic information of DNA reassembly of matching proteins. The part of the cell where proteins are built up, is called ribosome. .
4.4) Other nutrients
There are many other important nutrients, without which it would not survive - for example water, salts , electrolytes, vitamins , trace elements , dietary fiber, phytochemicals , minerals . Since I am here primarily concerned with energy metabolism, I have not dealt with these materials.
Links:
- " drinking in sports ," Dr. Moos
- " The daily water demand ," Dr. Moos
4.5), energy-, calorie
calorie
in the field of nutrition. common unit calorie (cal or kcal) is actually outdated. Valid the SI unit joule (or Was, Nm). 1 cal is the amount of energy to 1g water to heat up 1K. 1 joule is the energy to make 1 watt for 1 second to 1 meter wide and apply a force of 1 Newton. Approximately applies: 1 cal = 4.2 J.
condensing
The physiological calorific value is the amount of energy the body can gain from a given quantity of food. Normally the value is specified in kJ/100g or kJ/100ml. Order pasta: about 1500kJ/350kcal per 100g.
BMR
As ' BMR ' refers to the amount of energy required for a healthy body at 28 ° C on the vital functions to maintain. The basal metabolic rate is dependent on many factors and should therefore be seen as a benchmark: about 90kJ/kg or 21kcal/kg in women and about 100kJ/kg or 24kcal/kg in men - women are working ever more efficiently than men.
Links:
- " sensible diet," Dr. Moos
- " diet and nutritional supplements in sport ," Dr. Moos
5) photosynthesis
And how does the energy in the oatmeal? It is basically the light of the sun that drives us. The plants convert light energy through photosynthesis, the CO2 and water into O2 and glucose.
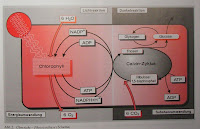 in plant cells, ATP also serves as an energy source. The processes in the human cell to run in the plant cell with virtually no other way around. In the chlorophyll-bearing plants of the cell components, hydrogen atoms of water and carbon atoms of the CO2 molecules are split off and on carrier (eg ADP / ATP) transfer. From that carrier molecules, they are in a closed chain of chemical reactions (Calvin cycle ) built into glucose (illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper).
in plant cells, ATP also serves as an energy source. The processes in the human cell to run in the plant cell with virtually no other way around. In the chlorophyll-bearing plants of the cell components, hydrogen atoms of water and carbon atoms of the CO2 molecules are split off and on carrier (eg ADP / ATP) transfer. From that carrier molecules, they are in a closed chain of chemical reactions (Calvin cycle ) built into glucose (illustration from ' basic issues of food ' by Cornelia A. Schlieper). removal efficiency is surprisingly low - only 0.8% of the incident light energy is converted into chemical energy - And of them produce large amounts of organic material - per hectare hardwood forest occur, for example, about 12 tons per year, total on Earth about 150 billion tons per year.
 in the sun, the energy mainly in the fusion of hydrogen atoms is released to form helium. The mass of a helium nucleus is smaller than the sum of the two hydrogen nuclei - the difference will be released in the form of radiant energy. It becomes so much radiated energy that we keep things in 150 million km (distance of the Earth) about 1400 watts per square meter . Every second in the core of the sun about 564 million tons of hydrogen are converted to 560 million tons of helium. The difference of 4.3 million tons of matter per second is emitted as energy - and that has Millliarden of years. For comparison - a swimming pool with Olympic-sized (50 x 25 x 2 meters) containing 2500 tons of water. The sun converts every second equivalent of 1720 Olympic swimming pool water into radiation energy.
in the sun, the energy mainly in the fusion of hydrogen atoms is released to form helium. The mass of a helium nucleus is smaller than the sum of the two hydrogen nuclei - the difference will be released in the form of radiant energy. It becomes so much radiated energy that we keep things in 150 million km (distance of the Earth) about 1400 watts per square meter . Every second in the core of the sun about 564 million tons of hydrogen are converted to 560 million tons of helium. The difference of 4.3 million tons of matter per second is emitted as energy - and that has Millliarden of years. For comparison - a swimming pool with Olympic-sized (50 x 25 x 2 meters) containing 2500 tons of water. The sun converts every second equivalent of 1720 Olympic swimming pool water into radiation energy. 6 ) sources
Wikipedia
the world's most brilliant website
 basic issues of food
basic issues of food Cornelia Schlieper
publishing trade and technology
source. Eg. publishing trade and technology
A book that I like very much. The clear illustrations make it possible for lay people to go into the topics. The book also increases a little further in-depth than eg. the book by Peter Konopka, but remains practical enough that even the more complicated sections should be read with pleasure.
 sports physiology
sports physiology Horst de Marees
Publisher Strauss
sources, for example. Amazon
A book for many long nights. Concentrated sports theory to approximately 800 pages. The issues extend beyond nutrition and metabolism. It is for example. Chapter on performance diagnostics, respiratory, cardiovascular, sports in the level or about diving and much more.
 manual sports nutrition
manual sports nutrition Geiss KR, M. Hamm
rororo Publisher
sources, for example. Amazon
also a great introduction to the basics of nutrition, metabolism and physiology. The focus is on theory.
 Biochemistry for unsuspecting
Biochemistry for unsuspecting Antje Galuschka
S. Hirzel Verlag
A great, in theory, more focused book that is free to paperc.de available online. The theme of the metabolism also lead for example. on topics such as genetic engineering and the immune system.
 sports nutrition
sports nutrition Peter Konopka
BLV Verlag
sources, for example. Amazon
also a great book. The focus is less on the deep theory as to the application in various sports (endurance, strength, endurance sports, etc.)
Optimized Endurance Training
 Neumann, Pfützner, Berbalk
Neumann, Pfützner, Berbalk publisher Meyer & Meyer
sources: eg . Amazon
The food theme is 'wide-treated side show'. The book offers but in addition to nutrition and metabolism an attractive entry into adjacent areas such as Trainingsplaung and regeneration.
Challenge Race Across America
Michael Nehls (Finisher 2008), Uwe Geissler
 Delius Klasing Verlag, 2009
Delius Klasing Verlag, 2009 sources, for example Homepage Michael Nehls (signed edition available), Amazon
The book I have mentioned several times in postings. There is also a detailed chapter on nutrition in ultra-sports. When Raceacross America I find the importance proper nutrition remarkable. The amount of calories that can accommodate the digestive system determines the performance of drivers. Through much of the route can only bring the power to the road you again also can hold. For the vast majority of sports, bring the power from before (in glycogen or fat) in the body of stored energy.
other interesting websites
- Dr. Moos , very interesting publications on the subject of nutrition and metabolism during exercise.
- Science of Sport , detailed blog by Ross Tucker and Jonathan Tucker (two sports-PhDs), often with endurance sports themes, such as nutrition in the Tour de France .
- Google Scholar provides many scientific publications of sports-Unis
- lectures at the University of Tübingen , hundreds of hours of video recordings of lectures (each 45 min), for example.
- Biochemistry 1 (15x), including hour 9 (TCA cycle)
- Biochemistry 2 (35x), etc. Hour 1 (proteins), from hour 22 (carbohydrate metabolism)
- Biochemistry 3 (45x), including Hour 1 (carbohydrate metabolism)
- Biochemistry 4 (35x), among other things hour 34 (muscles)
- Cell Biology 1 (20x), among other things hour 9 (mitochondria)
- Plant Physiology (41x), among other things. hour 10 (photosynthesis)
- Lectures4you : collection of links to freely available scripts / videos of lectures of various universities
- online vorlesungen.de : Links above, links to many prestigious universities such as eg. Berkley , eth Zurich
7) Conclusion
With every page I read about these topics, I find it impressive how good and stable, the body - these highly complex biochemical factory - so many years of life (most people) is working. It's amazing how interlock mechanisms and regulated. It is amazing how much energy the sun releases. It's an incredible gift to be able to live in such a world.